In December 2021, Sanyo Chemical Group declared its support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). We are working to disclose information appropriately in line with the four areas of disclosure recommendations of the TCFD: governance, strategy (transition plan, scenarios), risk management, and metrics and targets. We also assess the impact of climate change risks and opportunities on related financial indicators over time and reflect this in our management strategies.
Based on government policy, we have steadily reduced our CO2 emissions since FY2017. Our sustainability action plan aims to reduce CO2 emissions by 50% by 2030 (compared to FY2013) and achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, and we are actively working towards this goal across the entire Group. Furthermore, we will contribute to social sustainability and enhance our corporate value by fulfilling our responsibility as a chemical manufacturer to develop products that not only reduce CO2 emissions within the Group but also help reduce CO2 emissions throughout the entire supply chain.
Governance
Climate change governance is part and parcel of sustainability governance. In FY2024, the Sustainable Management Committee met three times and reported on climate change initiatives twice.

Strategy
When formulating our climate change strategy, we conduct scenario analysis in line with TCFD recommendations. The scenarios selected include a 1.5°C scenario that involves transitioning to a decarbonized society, as well as a 4°C scenario that sees economic growth prioritized globally.
Scenario Concept
*Horizontally scrollable
| 1.5°C scenario |
A decarbonization transition scenario that limits climate change with a 1.5°C rise in global average temperature (Reference) Long-term outlook by the International Energy Agency: “Net Zero Emissions by 2050” |
| 4°C scenario |
Economic growth scenario in which the global average temperature rises by 4°C and climate change progresses. (Reference) Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC AR6) "SSP5-8.5" |
The kind of world that we anticipate
*Horizontally scrollable
| The kind of world that we anticipate in the 1.5°C scenario |
Top priority placed on the realization of a decarbonized society, and implementation of an ambitious climate change policy
|
|---|---|
| The kind of world that we anticipate in the 4°C scenario |
Fossil fuel-dependent economic growth is our top priority, with no additional climate change measures to be implemented.
|
Risk management
We are considering myriad measures that the Group can take in response to the risks and opportunities associated with climate change impact according to various scenarios. Since conducting scenario analysis for FY2022, we have been continuously refining our approach. In FY2024, we conducted quantitative analysis to assess the impact of selected risks and opportunities, taking into account the time frame involved. We have listed the risks and opportunities common to all our businesses, as well as those specific to each business. The timeline classifies the timing of the risks and opportunities that will affect us as short term, medium term, or long term. The monetary impact assessment classifies the degree of impact as high, medium, or low.
Anticipated climate change factors (common to all businesses)
We anticipate that regulations such as carbon pricing policies aimed at decarbonization will become stricter, and that there will be a shift in demand toward materials suitable for decarbonization. We are exploring opportunities to create new markets by utilizing bio-based resources and sustainable resources. Furthermore, we anticipate the emergence of innovative technologies that will lead to a circular and decarbonized society. We believe that the development of technologies that utilize bio-based and recycled raw materials, as well as the development of low-carbon and highly energy-efficient processes, will ultimately strengthen our competitive advantages while also addressing the risks of relying on conventional production technologies.
In addition, we believe that the use of support measures and subsidies that recognize environmental contributions both domestically and internationally could help drive business transformation, and that appropriately disclosing environment-related information and responding to external evaluations are important.
Extreme weather and natural disasters caused by climate change pose risks that could disrupt supply chains for raw materials and logistics and affect our production systems. However, we will strive to improve our reliability as a company by regularly updating our business continuity plans and rebuilding our logistics networks, while also contributing to society by expanding our range of products related to disaster preparedness, sanitation, and post-disaster recovery.
Countermeasures Common to all Businesses Concerning the Risks and Opportunities of Climate Change
| Classification | Scenario | Climate change classification | Impact of climate change risks | Timeline | Impact assessment | Countermeasure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | 1.5°C | Policies and regulations | Raising of carbon tax | Increase in energy procurement costs | Medium to long term | High |
|
| Energy conservation and low-carbon regulations | Mandatory use of recycled raw materials | Medium to long term | Medium |
|
|||
| Policies | Loss of market share due to changes in export region regulations | Medium term | High |
|
|||
| Relocation or withdrawal of production bases due to changes in national policy | Short term | High |
|
||||
| Technologies | Contribution to the environment | Increase in demand for recyclable products | Medium to long term | High |
|
||
| Market | Market changes | Fragmentation of energy sources and raw materials due to policy divergences among countries | Medium to long term | High |
|
||
| Changes in consumer behavior | Changes in demand for low-carbon products | Long term | Low |
|
|||
| Reputation | Industry criticism | Capital withdrawal and loss of business due to disregard for environmental issues | Short, medium, long term | High |
|
||
| Lawsuits | Environmental degradation caused by fossil fuels | Long term | High |
|
|||
| 4°C | Acute risks | Natural disasters (typhoons, heavy rain, etc.) | Supply chain disruption, damage to company facilities | Short, medium, long term | High |
|
|
| Chronic risks | Natural disasters (Drought, rising temperatures, etc.) |
Water intake restrictions due to droughts, etc. | Long term | Low |
|
||
| Opportunities | 1.5°C | Policies and regulations | Energy conservation and low-carbon regulations | Increased investment costs for energy-saving equipment | Long term | High |
|
| Technologies | Contribution to the environment | Increase in ethical consumption due to frugality | Medium term | Medium |
|
||
| Market | Market changes | Potential for niche markets | Long term | Low |
|
||
| Reputation | Industry criticism | Rising environmental awareness in the BtoC market | Short term | Low |
|
||
| Lawsuits | Requests for transparent disclosure of environmental information | Medium to long term | Low |
|
|||
| 4°C | Acute risks | Natural disasters (typhoons, heavy rain, etc.) | Increased demand for products during natural disasters and severe weather | Short, medium, long term | Low |
|
|
| Chronic risk | Natural disasters (Drought, rising temperatures, etc.) |
Changes in lifestyles due to rising average temperatures | Short, medium, long term | Low |
|
||
Anticipated climate change factors (specific to each business)
With growing environmental awareness throughout society, there are concerns that products with a high environmental impact will not meet with public approval. On the other hand, we believe that actively developing products that contribute significantly to the environment will ultimately enhance corporate value. From the perspective of product life cycles, it is essential to develop and promote environmental performance chemicals that offer superior environmental performance such as high performance, long life, and light weight in order to achieve a carbon-neutral society.
By melding external knowledge with our existing and newly acquired strengths, we aim to develop products that benefit society and that advance global environmental sustainability while improving convenience and comfort.
Countermeasures Specific to Each Business Concerning the Risks and Opportunities of Climate Change
*Horizontally scrollable
| Classification | Scenario | Climate change classification | Impact of climate change risks | Timeline | Impact assessment | Countermeasure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | 1.5°C | Policies and regulations | Energy conservation and low-carbon regulations | Mandatory use of bio-based mass raw materials | Long term | Medium |
|
| Technologies | Contribution to the environment | Uncertainty about supply and demand for materials derived from edible sources | Medium term | High |
|
||
| Market | Market changes | Increasing demand for certification | Medium term | Low |
|
||
| Changes in consumer behavior | Declining sales of gasoline and hybrid vehicles | Medium to long term | High |
|
|||
| Changes in consumer tastes | A shift in values from things to experiences | Long term | High |
|
|||
| Reputation | Industry criticism | Reduced transactions with global procurement companies | Medium to long term | High |
|
||
| Lawsuits | Lawsuits against a chemical production base in an urban area | Medium to long term | High |
|
|||
| 4°C | Acute risks | Natural disasters (typhoons, heavy rain, etc.) | Quality deterioration due to temperature control failure caused by power outages | Short, medium, long term | Low |
|
|
| Chronic risks | Natural disasters (Drought, rising temperatures, etc.) |
Shortage of natural resources | Medium term | Medium |
|
||
| Opportunities | 1.5°C | Policies and regulations | Introduction and increase of carbon taxes | Proliferation of CCUS Increased demand for products that help avoided CO2 emissions |
Long term | High |
|
| Energy conservation and low-carbon regulations | Expansion of the market for products that help avoided CO2 emissions | Medium to long term | Medium |
|
|||
| Policies | Flue gas emissions regulations | Long term | High |
|
|||
| Technologies | Contribution to the environment | Transition from gasoline vehicles to electric vehicles | Medium term | High |
|
||
| Market | Market changes | Expansion of market for products using bio-based raw materials | Medium term | Medium |
|
||
| Expansion of preventive health business and growing need for home medical care | Medium term | Medium |
|
||||
| Changes in consumer behavior | Increasing demand for electric vehicles (promoting the lightweighting of vehicle batteries) | Medium to long term | High |
|
|||
| Changes in consumer tastes | Growing environmental consciousness in the daily necessities market | Medium to long term | Low |
|
|||
| Reputation | Industry criticism | Requests for transparent disclosure of environmental information | Long term | Low |
|
||
| Lawsuits | Criticisms of the petrochemical business | Long term | High |
|
|||
| 4°C | Acute risks | Natural disasters (typhoons, heavy rain, etc.) | Increasing demand for heat-insulating paint | Long term | Low |
|
|
| Chronic risks | Natural disasters (Drought, rising temperatures, etc.) |
Expansion of the market for agricultural products that are resistant to environmental changes | Medium term | Medium |
|
||
| Increasing demand for water quality improvement due to deteriorating water quality | Short term | Low |
|
||||
- The timelines are classified into short-term, medium-term, and long-term periods based on the timing at which risks and opportunities specific to our business characteristics become apparent.
Short term: Less than one year
Medium term: Less than 3 years, but 1 year or more
Long term: 3 years or more - Degree of monetary impact is classified into high, medium, and low.
High: Impact on profits is 1 billion yen or more
Medium: Impact on profits is from 100 million yen to less than 1 billion yen
Low: Impact on profits is less than 100 million yen
Indicators and targets
New Medium-Term Management Plan 2025 lays out various indicators and targets for efforts aimed at solving environmental issues.
One of these is an indicator for reducing greenhouse gas emissions (Scopes 1, Scope 2). Along with cogeneration and solar power generation, we will engage in Carbon dioxide Capture and Utilization (CCU) and utilize green hydrogen.
The other indicator is for expanding our lineup of products aimed at contributing to carbon neutrality.
As outlined in our management policy for achieving our vision for 2030, WakuWaku* Explosion 2030, we will work to reduce CO2 emissions by actively promoting sustainability management through means such as conducting a fundamental review of our business portfolio.
- "WakuWaku” is the Japanese word which express positive, bright, up-lifting feeling inspired by inner motivations and/or own wills.
Scope 1 and Scope 2: CO2 emissions from facilities
The Group established the Action Policy Concerning the Kyoto Protocol in 2005 when the Kyoto Protocol came into effect, and has since been working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions at each of its domestic facilities by increasing energy usage efficiency, improving production processes, and using alternative fuels.
In FY2018, we implemented a management policy to focus on the sale of high value-added products. This led to our discontinuing the sale of low value-added products, resulting in a decrease in production. As a result of changes in our product mix, our CO2 emissions per unit of domestic production has begun to decrease. In addition, the decision to withdraw from the superabsorbent polymers business in FY2023 and the resulting significant change in our business portfolio are expected to enable us to significantly reduce CO2 emissions from our own facilities in FY2024 and beyond, enabling us to achieve our "50% reduction in CO2 emissions by FY2030 (compared to FY2013)" goal ahead of schedule. The Group will continue to promote initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Going forward, we will focus on our Nagoya and Kashima factories, which have the highest CO2 emissions within the Group. As a measure to reduce CO2 emissions, we will consider utilizing CCU, switching to energy sources such as hydrogen, and fundamentally reviewing the manufacturing process on a per-product basis.
CO2 emissions by scope (Scope 1, Scope 2): Results and targets

Roadmap toward Carbon Neutrality
As a measure to reduce GHG emissions, we will engage in energy transition and efficiency (introduce energy management, deploy solar power and green hydrogen production facilities, and expand cogeneration) and review manufacturing processes. We also aim to become “net zero emissions by 2050” by introducing CCU.
*Horizontally scrollable

Emissions through the supply chain (Scope 3)
We have calculated direct emissions from fuel use and others (Scope 1), indirect emissions from the use of electricity, heat, and steam supplied by others (Scope 2), and emissions through the supply chain (Scope 3).
In FY2023, emissions from our facilities (Scope 1, Scope 2) were 231 thousand tons, while emissions through the supply chain (Scope 3, Category1–7, 12) were 1,911 thousand tons. CO2 emissions from purchased raw materials and CO2 emissions from the disposal of finished products using our products account for 53% and 39% of total Scope 3 emissions*, respectively.
*Horizontally scrollable
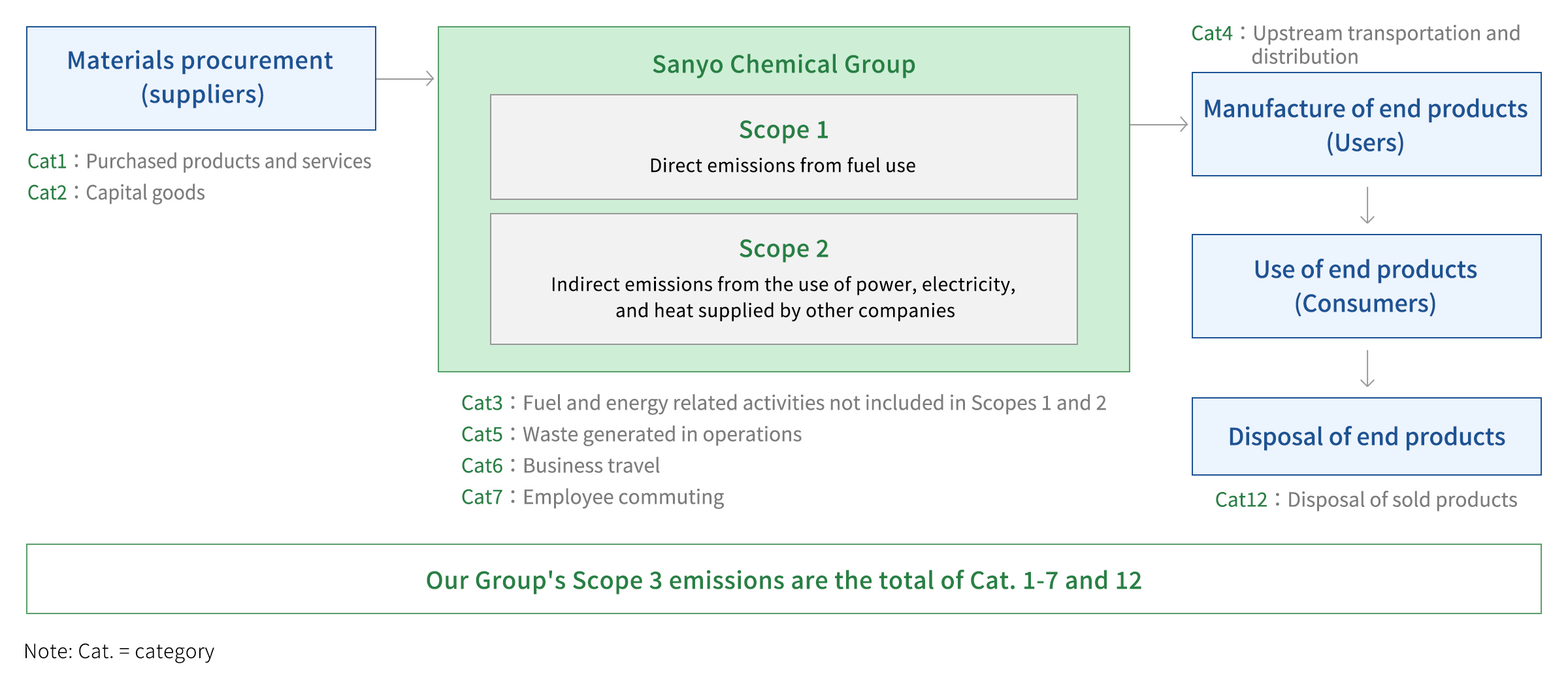
- Reporting on transportation is optional in both the Scope 3 Standard and the Basic Guidelines.
- Transportation is not included in accounting boundary in the Scope 3 Standard and the Basic Guideline.
However, operators may include it in this emissions accounting.
(Source) Minister of the Environment
- Total Scope 3 emissions: CO2 emissions from the use, processing, and transportation of our products at and to our customers' sites are not calculated due to the difficulty of collecting the necessary data.
Starting in FY2022, we use a CSR/Sustainable Procurement Self-Assessment Questionnaire formulated by the Global Compact Network Japan to reduce CO2 emissions through the supply chain.
Toward the future
The Group will appropriately disclose environmental information and fulfill its accountability to all stakeholders. By recognizing the impact that risks and opportunities from multiple climate change scenarios will have on our business activities, and by preparing countermeasures, we will improve the resilience of our business and continue to conduct business activities in accordance with the Company Mission. In addition to achieving carbon neutrality within our company by 2050, we will also contribute to reducing CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain and strive to realize social sustainability.